
In today’s article we’ll be looking at another management model, Vroom’s Expectancy Theory.
In this post we’ll cover
- What is Vroom’s Expectancy Theory?
- Who is Victor H Vroom?
- What are the key elements of Vroom’s Expectancy Theory?
- How is Motivational Force Calculated?
- How is Expectancy Theory Utilised in Business?
- Benefits of Vroom’s Expectancy Theory
- Issues Associated with Vroom’s Expectancy Theory
Ok let’s get to it.
What is Vroom’s Expectancy Theory?
Vroom’s Expectancy Theory assumes that our motivation is influenced by a combination of factors that all impact one another. These factors, including personality, skills, support and experience, affect our beliefs in three distinct categories;
- Expectancy,
- Instrumentality and
- Valence.
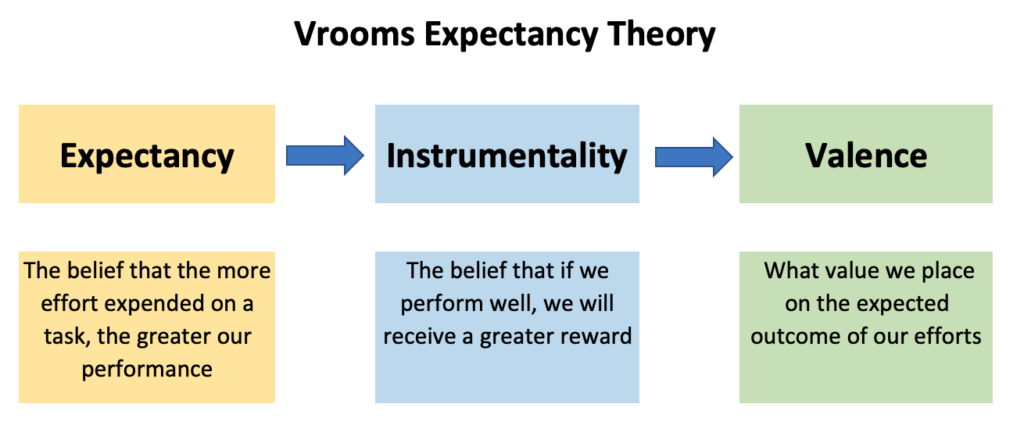
Expectancy is essentially the belief that the more effort expended on a task, the greater our performance will be.
This belief is affected by various factors, including whether we have the correct resources and skills available and whether we receive sufficient support.
Instrumentality goes a step beyond this and relates to the belief that if we perform well, we will receive a greater reward. This belief is shaped by things like whether we have a clear understanding of the relationship between performance and reward, and whether we trust the individuals who decide on the outcome of our positive work.
Thirdly, valence refers to whether we place a great deal of value on the expected outcome of our efforts. When considering valence, it is important to note the following key aspect:
“For positive valence to occur, we must prefer attaining the outcome to not attaining it.”
What does this mean? Well for example, if someone is motivated by praise and awards, they may not place a great deal of value on receiving a pay rise, however ‘positive’ this reward may be in theory.
Vroom’s Expectancy Theory offers a model that considers and separates three important factors influencing motivation; effort, performance, and outcomes.
Who is Victor H Vroom?
The founder of Vroom’s Expectancy Theory, Victor Harold Vroom, is a business professor at the Yale School of Management and an expert on behavior within organizations.
Victor H Vroom has a range of published books, including his seminal 1964 book, Work and Motivation, which vastly changed the way we think about leadership and decision making in the workplace.
What are the key elements of Vroom’s Expectancy Theory?
Effort → performance (E→P). E→P, otherwise known as effort-performance expectancy, refers to how likely we feel it is that our efforts will lead to the level of performance required.
Performance → outcome (P→O). P→O, or performance-outcome expectancy, deals with how probable we think it is that our successful performance will lead to the desired outcome.
V(R) outcome → reward. This is a measure of how much value we place on the rewards of a particular outcome, where -1 is avoiding the outcome, 0 is being indifferent to the outcome and +1 is welcoming the outcome.
How is Motivational Force Calculated?

According to Vroom, the motivational force can be calculated by combining the three key factors we have discussed above, such that:
Motivational Force (MF) = Expectancy x Instrumentality x Valence
How is Expectancy Theory Utilised in Business?
Vroom’s Expectancy Theory is perhaps best suited to the business environment, providing management teams with the vital knowledge that each employee’s motivation is a result of their own perceptions of the link between performance, outcome and reward.
This theory can, therefore, be beneficial when creating new motivational strategies within businesses, suggesting that systems in which rewards are highly correlated with outcomes may be most effective in boosting employee morale.
Crucially, Vroom’s Expectancy Theory also sheds light on the importance of providing meaningful rewards for employees.
Perhaps surveying team members to establish which types of reward they most value could be useful in improving overall motivation?
What’s more, Vroom’s Theory can be used in the creation of training programs. By providing courses that arm employees with both support and skills development, a business’ can increase their employees’ expectancy and in turn, their overall motivation.
Benefits of Vroom’s Expectancy Theory
The main benefits of this theory include:
• It is well-supported by scientific evidence, making it one of the most widely accepted theories of motivation.
• This theory offers a more thorough insight into motivation as opposed to theories like Maslow’s and Herzberg’s, which focus solely on the relationship between internal needs and effort expended.
• Although Vroom’s Expectancy Theory lends itself to the workplace, it can be utilized to assess and predict motivation in a variety of settings.
Issues Associated with Vroom’s Expectancy Theory
Despite the benefits of Vroom’s Expectancy Theory, there are also some key issues to consider.
For example, due to the nature of how motivational force is calculated, if any one of the three key factors (expectancy, instrumentality and valence) are zero, the entire result becomes zero, too. Can it be said that if someone does not value the reward of doing a particular task well, they will not be motivated to complete the task at all?
If there is a risk of punishment if a task is not completed well, could this also have an effect on motivation? Vroom’s Expectancy Theory could be seen as reductive in this sense.
As with any model, despite the relative thoroughness of theory, there are always further factors that could be considered important when calculating motivation.
Summary
We hope you enjoyed this article on Vrooms Expectancy Theory. What aspects do you consider lead to effective motivation? Perhaps you have tried some in your workplace? We’d love to hear about your results and any feedback you have in relation to Vrooms theory.
As always you can use Twitter or the articles comments section to contact us.
This article is part of our Management & Leadership Guide.