
In today’s article, we’ll cover Kolbs Learning Theory.
All of us learn in different ways; we need to devise ways of exploiting that. Kolb developed a theory of learning styles that offer valuable insight into effective teaching and training methods.
As individuals, we need to learn in ways that are both accessible to us and facilitate consuming and storing information.
In this article, we’ll look to cover:
- What are Kolbs Learning Styles
- Who is David Kolb?
- What is the Experiential Learning Cycle?
- Concrete Experience
- Reflective Observation
- Abstract Conceptualization
- Active Experimenting
- Four types of Kolb’s learning styles
- Diverging.
- Assimilating.
- Converging.
- Accommodating.
- Why is it important to understand learning styles?
- Benefits of Kolb’s learning styles
- Criticisms of Kolb’s learning styles
What are Kolb’s learning styles?
Kolb’s learning styles were initially formed as an extension of his experiential learning cycle.
This cycle identified four stages through which Learning occurs and laid the foundations for Kolb’s four learning styles to emerge.
These learning styles are titled:
- Diverging,
- Assimilating,
- Converging,
- Accommodating.
All four lend themselves to a specific element of the experiential learning cycle.
These learning styles are popular amongst educators and can offer valuable insight into effective teaching and training methods within educational settings and organizations alike.
Who is David Kolb?
David Kolb is a well-known psychologist and educational theorist, best known for his contributions to learning theory with the aforementioned experiential learning cycle and development of four learning styles that remain popular to this day.
Kolb was born in 1939 and graduated from Knox College in 1961. Upon graduation, he went on to study for his Ph.D in social psychology at Harvard University. He is currently still a Professor of Organizational Behaviour at Case Western Reserve University.
What is the Experiential Learning Cycle?
Kolb proposed a cyclical model of Learning, suggesting that effective Learning occurs when an individual is able to progress through this cycle.
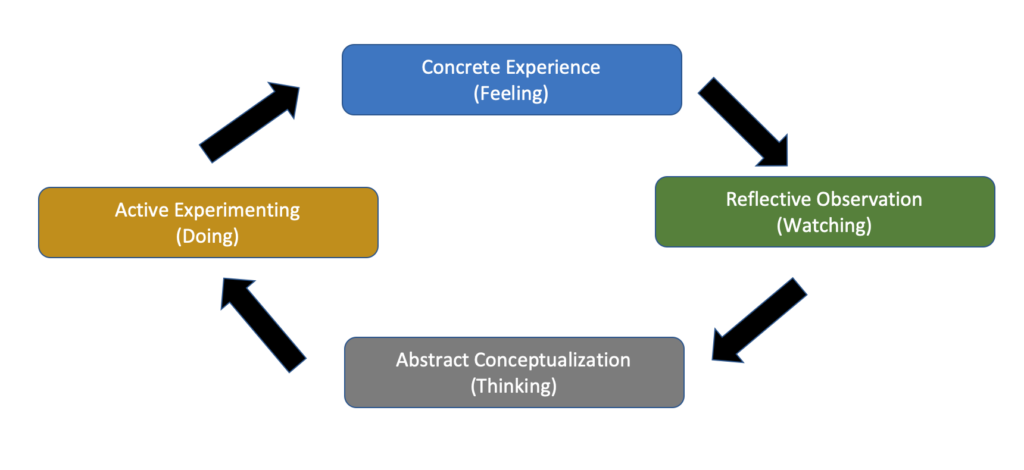
Kolb’s experiential learning cycle consists of four distinct stages.
Concrete experience, which involves doing something or having an experience.
Reflective observation, where the learner takes time to review or reflect upon their experience.
Abstract conceptualization, which involves coming to a conclusion or learning from their experience and reflection.
Active experimentation. In this stage, the learner plans and tries out what they have learned. This stage eventually leads to further concrete experience, and the cycle continues in this fashion, enhancing their Learning further.
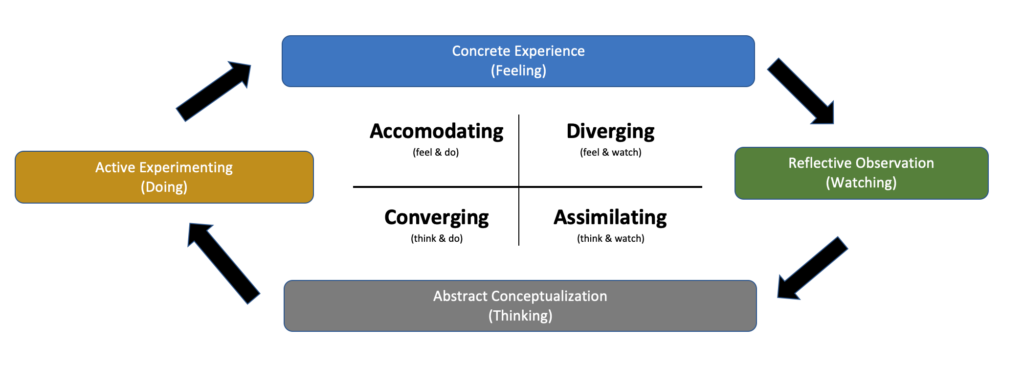
Each of Kolb’s ‘styles’ of Learning is particularly adept at a specific part of this cycle. For example, diverging learners tend to be competent at the concrete experience stage.
Four types of Kolb’s learning styles?
Kolb used his learning cycle, which we will discuss in more detail in just a moment, as a foundation for the development of four distinct learning styles.
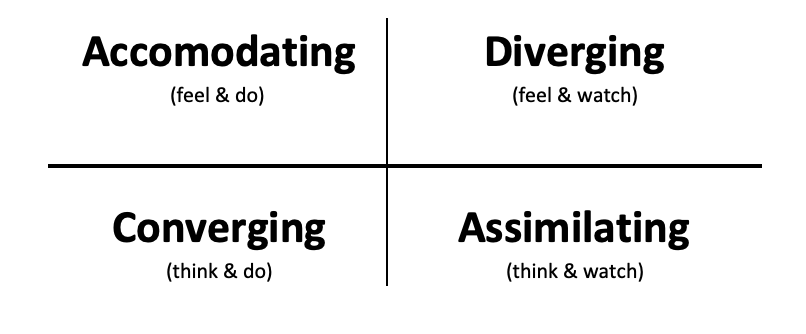
1. Diverging.
This group of learners is visually orientated and open to a range of different perspectives. They learn best by watching and imagining and are often sensitive and emotional. Activities in which they may perform well include brainstorming and other idea-generation tasks.
2. Assimilating.
These learners are more interested in tasks and concepts than people and tend to be good at exploring and analyzing models. They are great organizers and work best when given a clear explanation rather than a practical demonstration. Assimilating learners are more drawn to logical theories over practical approaches, and will likely enjoy lectures and readings.
3. Converging.
Those with a converging learning style are great at problem-solving. They always have practicality at the forefront of their mind and tend to prefer technical tasks to interpersonal relationships. They will likely enjoy jobs with practical applications that require technical ability.
4. Accommodating.
Similarly to the converging type, these people also have a practical outlook and often rely on intuition and gut feeling. This learning style is extremely common, and these learners prefer to analyze other people’s theories, rather than generating completely new ideas.
You can see how these factors influence the learning cycle in the diagram below:
Why is it important to understand learning styles?
In simple terms, the application of Kolb’s theories could lead to a more effective learning experience.
Kolb’s learning styles have greatly impacted the educational system, allowing teachers not only to provide students with learning opportunities that serve their personal learning style but to ensure that each stage of the experiential cycle is covered through learning materials.
Benefits of Kolb’s learning styles
• May lead to better educational outcomes and more positive learning experience in both schools and the work environment.
• Allows businesses and educators to create targeted and specific learning sessions to suit their students’ or employees’ personal needs.
• There is scientific evidence to support Kolb’s theory. For example, in 1973, Kolb and Goldman found that students who were studying for a degree that fit well with their learning style tended to show greater commitment to their field than those who were not.
Criticisms of Kolb’s learning styles
No model or theory is perfect; some criticisms of Kolbs learning styles include:
• It could be seen as reductive to categorize an individual as a certain ‘type’ of learner. It may be the case that learning style varies depending on the situation or subject matter, or someone may well be a combination of 2 or more of Kolb’s learning styles.
• The level of evidence in support of their existence has been much debated.
• Mark K. Smith suggested that Kolb’s theory should acknowledge the role of external factors and cultures that may also impact Learning.
Summary
Training & Learning is a crucial element of getting the best out of your workforce and as such, understanding the methods of executing training most effectively is key.
There are a variety of methods available, including Kolb’s, and before leaping into training programs, businesses should take a step back and assess which methods offer the best returns for their industry.
If you want to find out more about Kolb’s theory, I’d suggested you start with this great interview with David Kolb that you can find on Youtube.
As ever, we’d love feedback. What do you think of Kolb’s method? You can leave us comments below or message us via twitter.
This article is part of our Management & Leadership guide.